|
Contents
Image: Thinkstock |
These easy steps can prevent from itchy, oozing rashes.
Criminals
Like animals, many plants have defense systems to guard themselves. Some extract allergenic oils or juices. If you touch or brush against it, the contact triggers an allergic response that appears in two to 10 days as a red, swollen, itchy, blistered rash called allergic contact dermatitis. . Poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac are probably the most well-known for causing this problem, but there may be a protracted list of other culprits, akin to tomato plant leaves and plenty of flowers, including marigolds, chrysanthemums, poinsettias and Includes philodendrons.
Other plants protect themselves with spines and thorns. Roses and cacti are best known for them, however the tiny spikes are on many common plants, akin to some mosses, palms, and blackberry and raspberry bushes. The rash that results from contact with these spikes is comparable to contact dermatitis, but involves small puncture wounds and is known as mechanical irritant dermatitis.
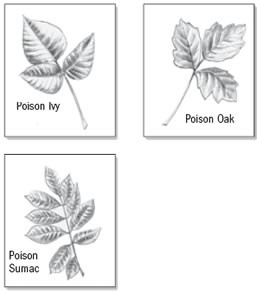
Know your poisons.
Example: Susan Aveshai Poison ivy and poison oak (above) are either |
Treatment
Dr. Arndt says the allergic response will go away by itself in about 10 days, but you'll likely want relief from a burning, itchy feeling. To relieve symptoms, he recommends applying a cool compress after which patting your skin dry. He also prescribes topical steroids. “Hydrocortisone is available over the counter, but it has low potency,” says Dr. Arndt. He says probably the most powerful creams are prescription-only — clobetasol (Cormax, Timvet) and flucainonide (Lidex).
You might want to apply the creams a number of times a day until the rash clears up. Dr. Arndt says the most effective option to apply creams is to clean the affected skin, pat it dry, after which apply the cream while the skin remains to be damp. It might be higher absorbed this manner.
Debunking the Poison Ivy Myth:1 Myth: Rash is contagious.Not true. It may look unpleasant, nevertheless it won't spread to yourself or one other person, even whenever you see blisters. Myth 2: If you've gotten it once, you're immune.Not true. Once you get it, you will certainly get it again since you might be allergic to it. Myth 3: You can get it by respiration.Sometimes true. You won't inhale the toxins in case you walk by it, but you'll have an allergic response if the plant is burning nearby and also you breathe within the fumes. |
Prevention
The easiest option to avoid one in every of these fibers is to guard yourself whenever you're outdoors. This means wearing protective clothing — long sleeves and pants — when gardening or spending time near potentially poisonous plants. Dr. Arndt also recommends using a thick pair of labor gloves. “The best gloves are heavy enough that they don't break in easily, but flexible enough that you can work with them,” he says.
Once you're back in, you may as well be lively. Use soap and water to clean your hands or any a part of your body that has come into contact with poisonous plants. “If you wash immediately, most of the plant oil will be reduced or gone,” says Dr. Arndt. “If you wait 10 to 15 minutes, half the oil will stop, if you wait an hour, none will come.”